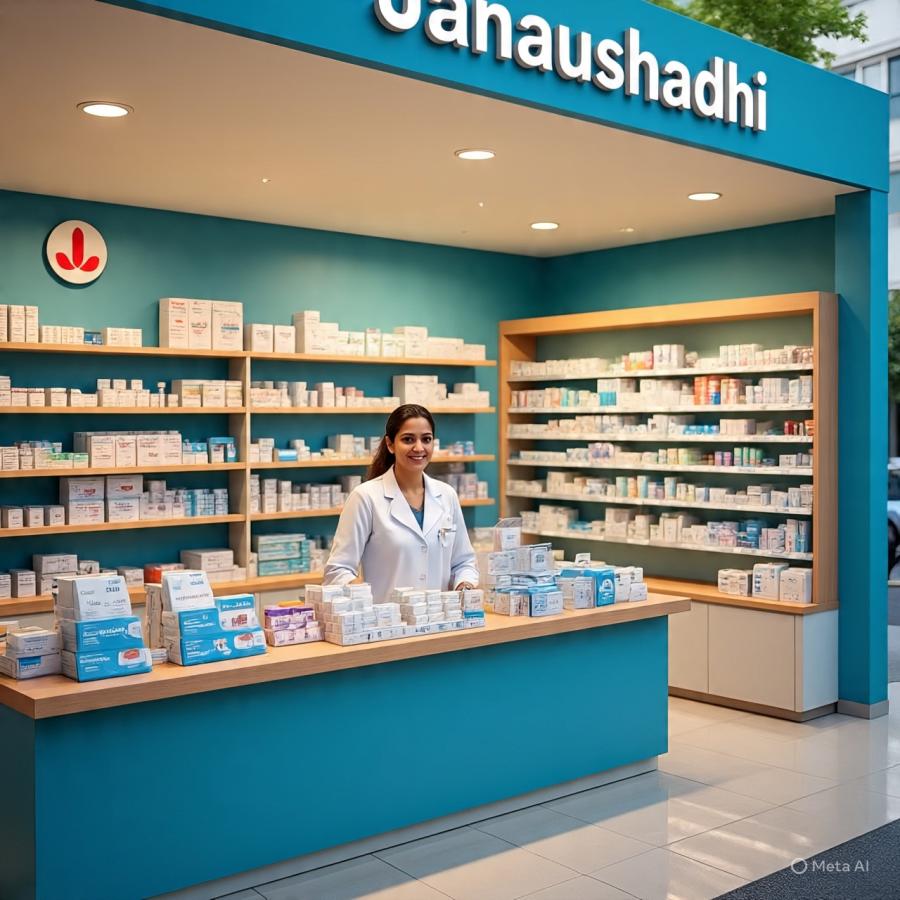
The Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) has emerged as a transformative initiative aimed at ensuring affordable healthcare for the Indian population. In a country where medical expenses often become a burden for millions, this scheme provides a cost-effective alternative through generic medicines sold at dedicated outlets known as Janaushadhi Kendras. With rising healthcare costs and limited accessibility to affordable medicines, the government’s initiative plays a crucial role in bridging the healthcare gap. Despite its success, several challenges remain that need to be addressed for better implementation and widespread acceptance.
The Vision Behind the Janaushadhi Scheme and Its Impact on Healthcare Costs
India has been a global leader in generic drug manufacturing, exporting affordable medicines to various countries. However, despite this advantage, access to affordable drugs within India has remained a challenge. The Janaushadhi Scheme was introduced to ensure that quality generic medicines are available to the general public at a fraction of the cost compared to branded drugs. This initiative aims to reduce the financial burden on patients while promoting the use of cost-effective alternatives without compromising on quality. By providing generic medicines at significantly lower prices, this scheme has saved consumers thousands of crores and reduced out-of-pocket medical expenses, which is a leading cause of financial distress in many Indian households.
Expanding Access to Affordable Medicines Through Janaushadhi Kendras
One of the primary objectives of the Janaushadhi Scheme is to make generic medicines accessible across urban and rural areas. The government has set up thousands of Janaushadhi Kendras across the country, ensuring that people have access to essential medicines without financial constraints. These stores are strategically located to cater to both urban and rural populations, where affordability often dictates healthcare choices. The presence of these centers has significantly improved the availability of medicines in areas where people previously had to rely on expensive branded drugs. With an ever-expanding network, the government aims to establish over 10,500 Janaushadhi Kendras to ensure wider accessibility.
Quality Assurance and the Effectiveness of Generic Medicines
One of the key concerns surrounding generic medicines is the perception that they are inferior to branded drugs. However, studies and medical research have repeatedly confirmed that generic medicines available under the Janaushadhi Scheme meet the required quality standards. These medicines undergo rigorous testing and adhere to the regulations set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other regulatory bodies.
A recent study on antihypertensive drugs found that patients who used generic medicines from Janaushadhi Kendras experienced the same level of effectiveness as those who used branded alternatives. Despite such findings, public awareness regarding the efficacy of generic medicines remains low, and more efforts are needed to dispel misconceptions surrounding them. Many healthcare professionals still hesitate to prescribe generic medicines due to preconceived notions about their quality, making it essential to spread awareness and build trust within the medical community.
Public Awareness and the Need for Better Promotion of the Janaushadhi Scheme
Despite the scheme’s numerous benefits, a significant percentage of the population remains unaware of the existence of Janaushadhi Kendras and the availability of affordable medicines. Studies indicate that nearly 40% of the public has little or no knowledge of Jan Aushadhi stores. Even among those who are aware, there is skepticism regarding the quality and effectiveness of generic medicines. This lack of awareness highlights the need for extensive promotional campaigns to educate people on the cost benefits and efficacy of these medicines.
Government initiatives, along with collaboration with healthcare professionals, can play a vital role in changing public perception. Conducting outreach programs, leveraging digital platforms, and engaging with local healthcare providers can help in disseminating accurate information. Increasing awareness among doctors and pharmacists is equally important, as their recommendations strongly influence patients’ choices. By incorporating information about Janaushadhi medicines in medical education and training, the government can ensure long-term sustainability and wider acceptance of the scheme.
Challenges Hindering the Full Potential of the Janaushadhi Scheme
While the scheme has achieved significant progress, several challenges continue to hinder its full potential. One of the primary issues is the uneven distribution of Janaushadhi Kendras across India. While urban areas have witnessed a steady increase in these centers, rural regions still struggle with limited access. This disparity limits the impact of the initiative, as the population in remote areas remains dependent on expensive branded medicines due to a lack of alternatives.
Another major concern is the frequent shortage of medicines at Janaushadhi Kendras. Inconsistent supply chains, logistical difficulties, and delays in procurement often result in stockouts of essential medicines. Patients who rely on these stores may face difficulties in accessing required medications, leading them back to costlier alternatives. Addressing these issues through a more streamlined supply chain and improved inventory management will be crucial in enhancing the efficiency of the scheme.
Additionally, while the government has ensured that the medicines sold through Janaushadhi Kendras meet quality standards, some consumers still express concerns about differences in composition and packaging compared to branded drugs. Strengthening quality control mechanisms and transparency in the manufacturing process can further build consumer confidence.
Economic Impact and Cost Savings Through Generic Medicines
The affordability of medicines under the Janaushadhi Scheme has resulted in massive savings for consumers. Generic medicines available through Janaushadhi Kendras are priced 50% to 90% lower than their branded counterparts. This reduction in cost has played a crucial role in making healthcare more accessible, especially for low-income groups and those without medical insurance. The impact is even more significant for individuals suffering from chronic illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases, who require long-term medication.
A cost analysis revealed that the price difference between branded and generic medicines can be as high as 80%, allowing families to allocate their financial resources to other essential needs. The savings generated through the scheme also contribute to reducing the overall economic burden on the healthcare system. By lowering dependency on expensive drugs, the initiative helps in minimizing government expenditure on subsidized medicines, thereby freeing resources for other public health initiatives.
The Future of the Janaushadhi Scheme and the Road Ahead
As the government continues to expand the reach of the Janaushadhi Scheme, several measures can be taken to ensure its long-term success. Strengthening the distribution network, improving stock availability, and enhancing quality assurance mechanisms will be crucial in gaining public trust. Increasing the number of warehouses and optimizing logistics will help in ensuring the consistent availability of medicines across all regions.
Encouraging healthcare professionals to prescribe generic medicines and incorporating Janaushadhi products into public healthcare programs can further boost adoption rates. The scheme’s success ultimately depends on increased awareness, efficient implementation, and continuous improvements in accessibility and quality.
The Janaushadhi Scheme represents a significant step towards making healthcare more affordable and accessible for millions of Indians. By addressing the existing challenges and leveraging public-private partnerships, India can further strengthen its healthcare system and ensure that every individual has access to essential medicines at affordable prices. The future of the scheme lies in its ability to scale efficiently, build consumer confidence, and promote the adoption of generic medicines as a viable alternative to expensive branded drugs.
With continued government support, strategic awareness campaigns, and active participation from healthcare professionals, the Janaushadhi Scheme can transform India's pharmaceutical landscape and provide a sustainable solution to the issue of high medical costs. By embracing the potential of generic medicines and enhancing public trust, India can move closer to achieving universal healthcare and reducing the financial burden of medical expenses on its citizens.
By Gautam Jha
Managing Editor